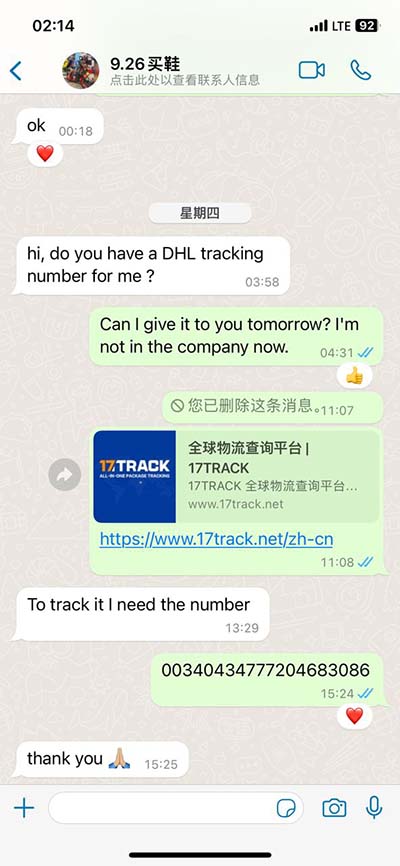
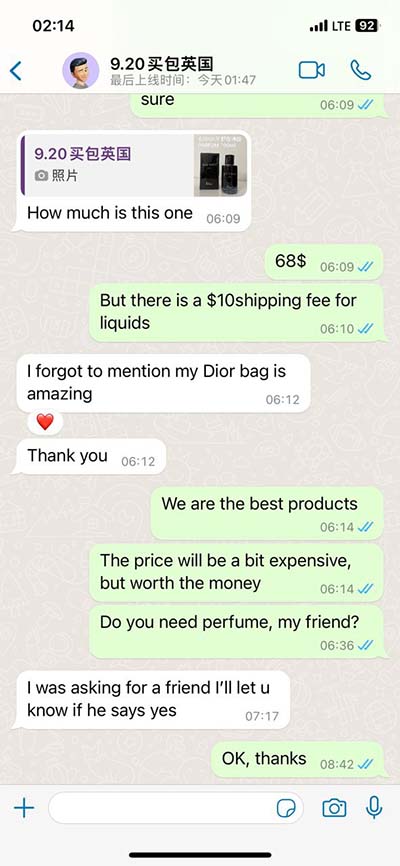
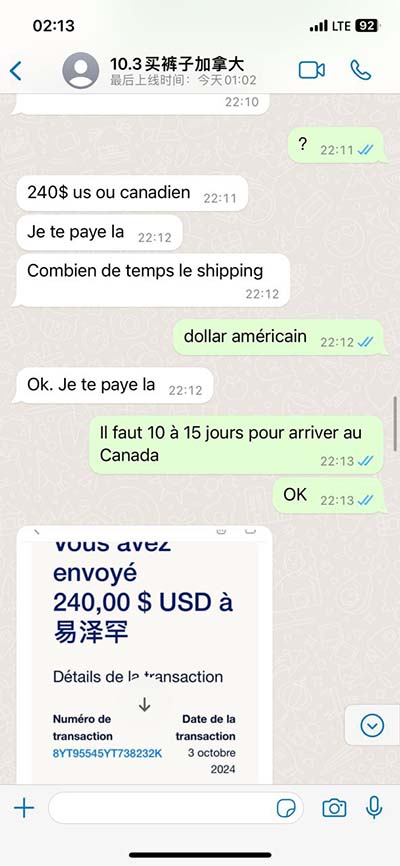
lv kj | kjv leviticus 25 lv kj These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kJ⋅mol −1. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Nepatīk, ka Cenuklubs cenas uz cenu zīmes var atšķirties uz to, kas rādās pie kases. Tas būtu ok, ja pie kases cena būtu zemāka, bet tā jau nekad nenotiek. Kasierus vainot par to nevar, jo viņi tikai izpilda savu robota funkciju, bet tie, kas ir atbildīgi par cenu zīmju nomaiņu, iespējams, visu nevar paspēt.
0 · ununhexium element
1 · livermorio
2 · leviticus chapter 25 kjv
3 · latent heat of water chart
4 · latent heat of freezing water
5 · kjv leviticus 26
6 · kjv leviticus 25
7 · how was livermorium discovered
Buy GorillaGlides CB253 1 Inch Chair Sliders/Furniture Glide Floor Protectors (Set of 8 Glides) Self-Adhesive Screw-On Glides, for Sliding on Hard Surface Floors and Low-Pile Carpet, Round: Furniture Sliders - Amazon.com FREE DELIVERY possible on .
ununhexium element
These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kJ⋅mol −1. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms.
A lot of heat is required to vaporise a liquid, so the latent heat of vaporisation is large. When a gas cools and condenses into a liquid, a lot of heat energy is given out. Latent Heat of Vaporisation .
The amount of energy need to melt a kilogram of ice (334 kJ) is the same amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1.000 kg of liquid water from 0 °C °C to 79.8 °C °C. This .These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kJ⋅mol −1. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms.
A lot of heat is required to vaporise a liquid, so the latent heat of vaporisation is large. When a gas cools and condenses into a liquid, a lot of heat energy is given out. Latent Heat of Vaporisation .The amount of energy need to melt a kilogram of ice (334 kJ) is the same amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1.000 kg of liquid water from 0 °C °C to 79.8 °C °C. This example shows that the energy for a phase change is enormous compared to energy associated with temperature changes.In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ∆Hvap), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas.L is specific latent heat for a particular matter (kJ kg-1); Lv for vaporization and Lf for fusion. Note: The latent heat of water at 0 degree Celsius for fusion is nearest to 334 joules per gram or 79.7 calories per gram.
livermorio
The latent heat calculator helps you compute the energy released or absorbed during a phase transition like melting or vaporizing. In the text below, we explain what is specific latent heat and present a simple latent heat calculation. Specific latent heat is energy hidden in the internal structure of a substance.The first ionization energy of polonium, Po, is 812 kJ/mol. Is the first ionization energy of Lv expected to be greater than, less, than or equal to that of Po? Justify your answerThe heat of vaporization of water (Lv on the chart) is 2260 kJ/kg. Sample problem: How much energy is required to vaporize 700 g of water? Answer: Heat energy = mass times the heat of vaporization or. Q=m x L v. I have to make my units match up so I will convert 70 g to 0.700 kg. Q=m x L v = 0.700kg x 2260 kJ/kg = 1582 kJ.
A 3 kW kettle contains 2.0 kg of water at a temperature close to 100oC. Latent heat of vaporisation for water: Lv=2256 (kJ kg^-1) Q= Lv x mass.On a hot dry day, evaporation from a lake has just enough heat transfer to balance the 1.00 kW/m2 of incoming heat from the Sun. How many kilograms of water evaporate in 0.75 h from each square meter of the lake? You can assume the latent heat of vaporization for water here is Lv = 2414 kJ/kg.These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kJ⋅mol −1. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms.
A lot of heat is required to vaporise a liquid, so the latent heat of vaporisation is large. When a gas cools and condenses into a liquid, a lot of heat energy is given out. Latent Heat of Vaporisation .
The amount of energy need to melt a kilogram of ice (334 kJ) is the same amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1.000 kg of liquid water from 0 °C °C to 79.8 °C °C. This example shows that the energy for a phase change is enormous compared to energy associated with temperature changes.In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ∆Hvap), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas.L is specific latent heat for a particular matter (kJ kg-1); Lv for vaporization and Lf for fusion. Note: The latent heat of water at 0 degree Celsius for fusion is nearest to 334 joules per gram or 79.7 calories per gram.
The latent heat calculator helps you compute the energy released or absorbed during a phase transition like melting or vaporizing. In the text below, we explain what is specific latent heat and present a simple latent heat calculation. Specific latent heat is energy hidden in the internal structure of a substance.The first ionization energy of polonium, Po, is 812 kJ/mol. Is the first ionization energy of Lv expected to be greater than, less, than or equal to that of Po? Justify your answer
The heat of vaporization of water (Lv on the chart) is 2260 kJ/kg. Sample problem: How much energy is required to vaporize 700 g of water? Answer: Heat energy = mass times the heat of vaporization or. Q=m x L v. I have to make my units match up so I will convert 70 g to 0.700 kg. Q=m x L v = 0.700kg x 2260 kJ/kg = 1582 kJ. A 3 kW kettle contains 2.0 kg of water at a temperature close to 100oC. Latent heat of vaporisation for water: Lv=2256 (kJ kg^-1) Q= Lv x mass.
leviticus chapter 25 kjv
latent heat of water chart

rolex pendant necklace
Every sector (like Cephalon HQ) and level in Splatoon 2 has collectibles for you to find. The 32 sunken scrolls will add pages to the game’s backstory, and the 32 pieces of sardinium will let.
lv kj|kjv leviticus 25